Metal injection molding is a powder metallurgy process used to make metal parts. Although metal injection molding uses powder metal, it is different from conventional powder metal processing. The metal powder used for metal injection molding is 10-100 times smaller than the powder metal process. Similarly, the final product density of metal injection molding is higher. Applications of Chinese metal injection molded parts include surgical tools, car locks and actuators, firearm components, computer hard drives and electrical connectors.
Metal injection molding process
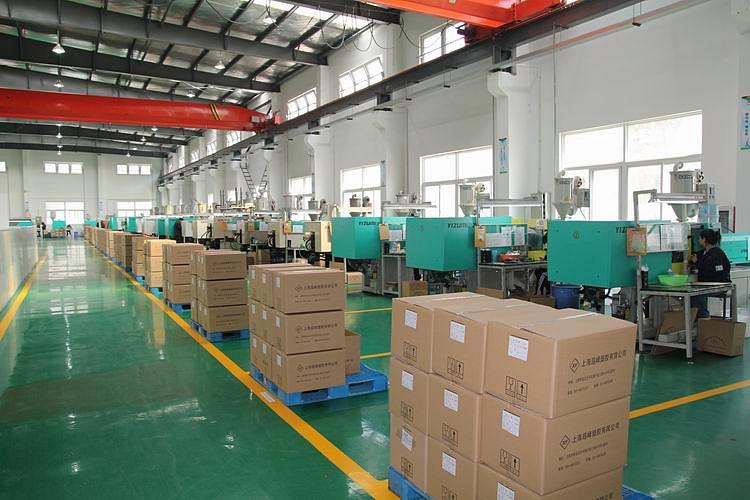
Metal injection molding is a rapidly evolving manufacturing method that bridges the gap between technology upgrades and related costs. The metal injection molding process includes five steps, mixing, injection molding, degumming, sintering, and part finishing.

In the mixing step, metal powder is usually mixed with a binder, and these metal powders are selected based on their strength and inherent abilities (such as impact strength, high and low temperature characteristics, abrasion resistance, mechanical properties, and hardness). By mixing powders, the goal is to make a composite material with all the advantages and benefits of metal incorporation, while making up for the shortcomings of independence.
Once the powder is mixed, a “raw material” is produced. This raw material is injected into Chinese injection molding in the same way as plastic or rubber injection molding is performed. Parts coming out of the injection phase are called “green” parts.
During the debonding phase of metal injection molding, the green body is immersed in a water bath to remove the binder that has entered the part matrix. In the cross-linking, the bonded green body is partially exposed to ultraviolet light, which thermally cures the binder used with the metal powder.
After the degumming phase is complete, place the part in the furnace and heat it above 2000 degrees Fahrenheit. This process is called sintering and melts metal parts into a solid shape. Finally, the sintered part is sent to the finishing stage, where burrs and surface defects are removed, and the finished product is transported.
Advantages of metal injection molding: high shape complexity, low cost, strict tolerances, high density, high performance.
Uses of metal injection molding:
This technology excels in applications that require complex shapes and high final characteristics, such as those that cannot be met by plastics or light metal alloys, such as high strength and density, excellent magnetic permeability, high temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Therefore, metal injection molding is most suitable for some of the following applications. Microelectronics packaging, automotive sensors and actuators, hand tools and hardware, computer heat sinks, oil well drilling tools, aerospace and engine fuel assembly manufacturing.
