Choosing a suitable tool steel supplier is crucial for both the mold maker, the mold user and the end user of the product.
In fact, in the early development of the mold industry in the course of the total, the early stages of the main use of carbon tool steel (such as T8, T10) or ordinary alloy steel, low performance, easy to wear, short life.
Processing performance is poor, heat treatment deformation, polishing performance in general, can not meet the demand for high-precision molds.
In the industry’s mid-term development, began to use alloy structural steel (such as P20, 718, NAK80, etc.), with good polishing performance, cutting performance and a certain corrosion resistance.
Mold life significantly improved to meet the production requirements of most of the middle and high-end plastic products.
Modern as well as began to high-performance, multi-functional, long-life direction.
Appearance of a large number of pre-hardened steel, corrosion-resistant steel, mirror polished steel, high temperature steel, powder high-speed steel and other special mold steel species.
The process is more advanced, such as vacuum melting, electroslag remelting, powder metallurgy, etc., to improve the purity and stability of steel.
This article focuses on high-grade plastic mold materials manufactured by the Austrian company Bai Lu.
Bai Lu is highlighted because it represents the world’s most advanced level of manufacturing in this field.
Additionally, the company produces a complete series of plastic mold materials, covering a wide range of applications.
Plastic mold steel types and types
special plastic mold steel
>surface hardening steel
The steel through carburization for surface hardening, and then quenched and tempered, so that the surface hardness of 62HRC or so, the heart is the slat martensite and get very high strength.
The excellent surface finish of the carburized steel is also due to its high purity and homogeneity of organization. Table 1 shows the chemical composition of the case-hardening steel.
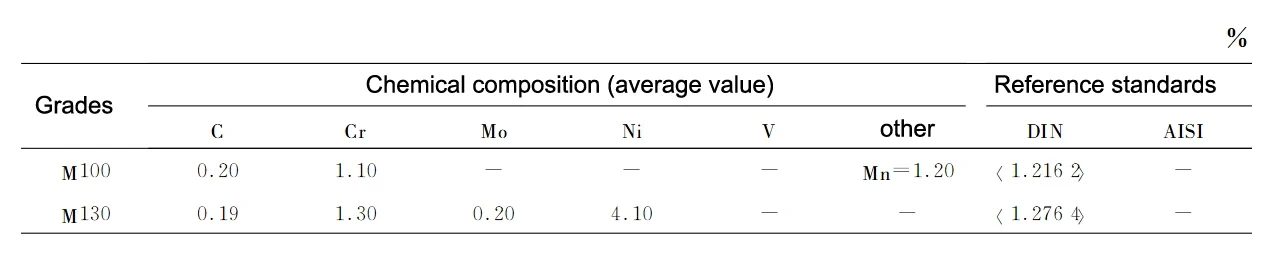
From the chemical composition, the steel belongs to the low carbon low alloy steel, M100 is equivalent to 20Mn, M130 is equivalent to 20Cr2Ni4, very suitable for carburizing treatment, has excellent hardenability, the heart is easy to strengthen.
>pre-hardened steel
Pre-hardened steel is quenched and tempered through a heat treatment process known as quenching and tempering. This pre-heat treatment brings the material into a pre-hardened state.
The resulting pre-hardened hardness falls within the ideal range required for plastic mold work. As a result, molds made from this steel do not require additional heat treatment and can be used directly.
This steel already possesses good abrasion resistance and compressive strength. The typical pre-hardened hardness ranges between 290 and 330 HB.
In some special cases, the upper limit of working hardness can reach up to 400 HB.
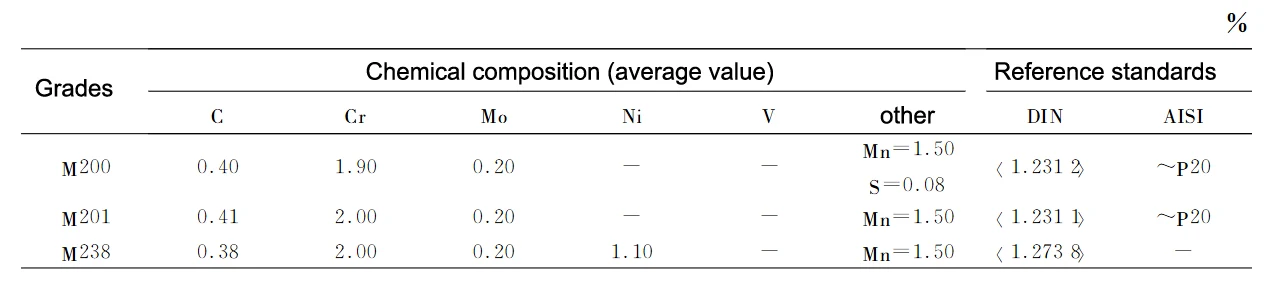
Table 2 shows the chemical composition of pre-hardened steel.
As can be seen from Table 2, the steel belongs to the medium carbon medium alloy steel, suitable for tempering heat treatment, so that the mold has both high hardness and very high strength.
> Precipitation hardening steel
After annealing and precipitation hardening treatment, has been pre-hardened, without heat treatment, high hardness, with good machinability and EDM properties.
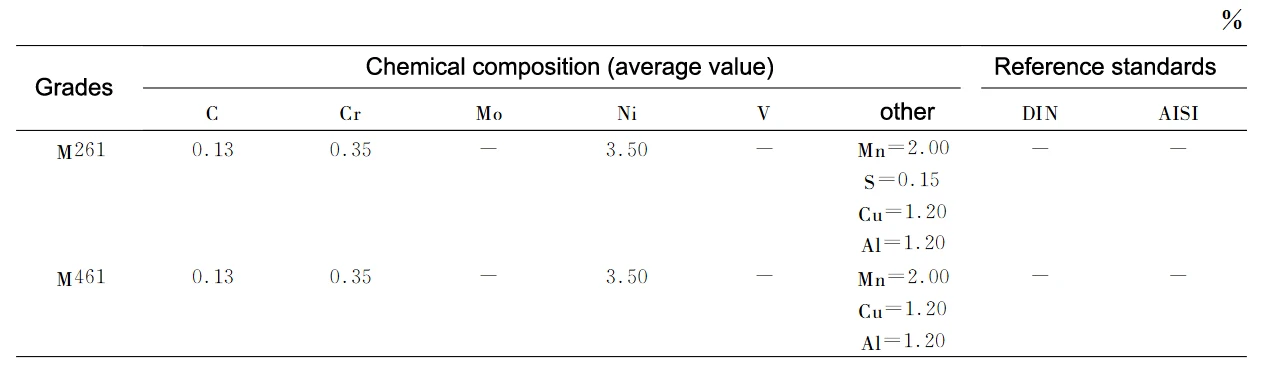
Pre-hardened hardness of about 40HRC, to achieve the use of plastic mold hardness. Table 3 for the chemical composition of precipitation hardening steel.
> Corrosion-resistant steel
This type of steel is divided into pre-hardened steel and heat treatment hardened steel 2 kinds.
Pre-hardened steel does not require additional heat treatment.
It can be processed and used directly after manufacturing. In contrast, hardened steel requires heat treatment.
It must be quenched and tempered before use. This type of steel belongs to the category of martensitic stainless steel.
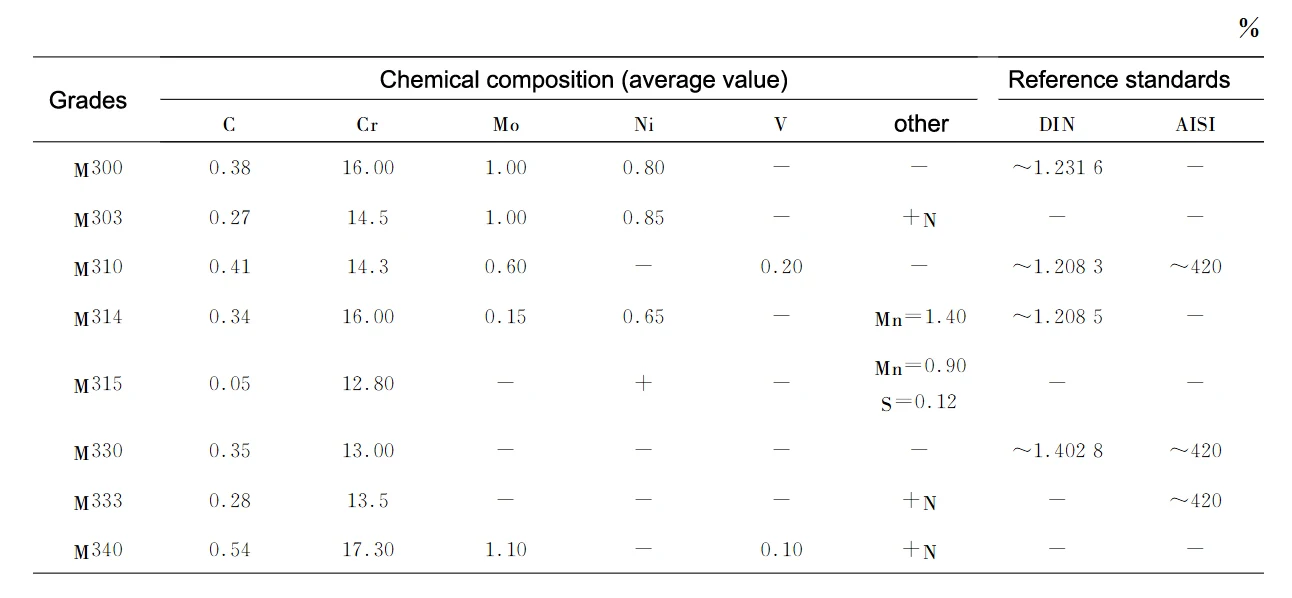
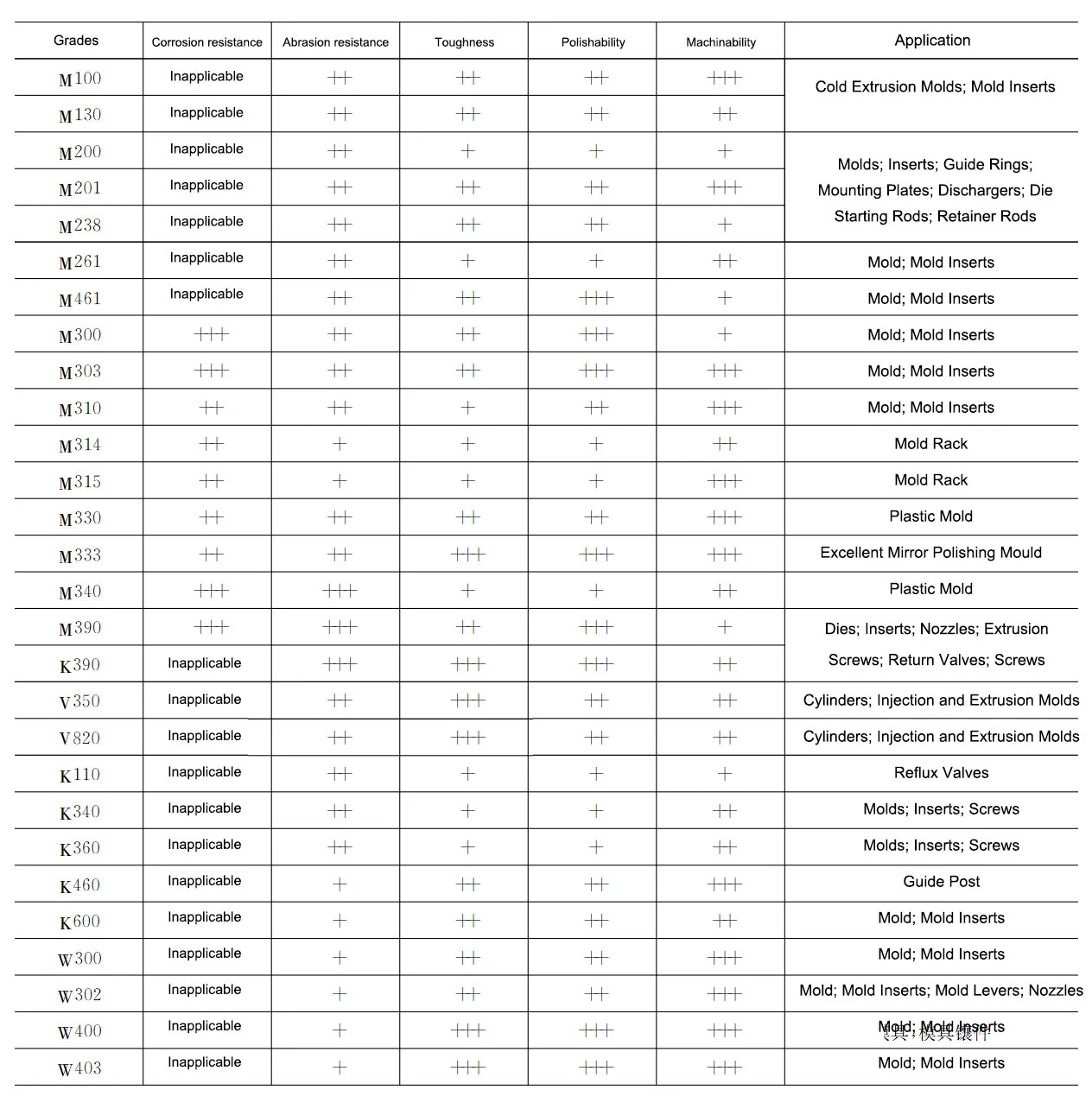
Table 4 for the chemical composition of corrosion-resistant steel, of which M300, M303, M314 and M315 for the pre-hardened steel, M310, M330, M333 and M340 for the heat treatment of hardened steel.
> Free Cutting Steel
Free cutting steel without Se, Te or Pb sulfur content of 0.08% to 0.30%, while the ordinary steel sulfur content does not exceed 0.030%.
Greatly increase the sulfur content is to improve the steel cutting chipbreaking capacity, thereby increasing the feed and improve machining efficiency.
From Table 2, 3 and 4 can be seen, M200, M261 and M315 should be easy to cut steel.
> Nitrogen-containing steel
At room temperature, nitrogen in ferrite has the greatest solid solubility; while at high temperatures, nitrogen in austenite has the greatest solid solubility.
A high-temperature austenite solid solution can absorb a large amount of nitrogen. After subsequent quenching and cooling, the austenite transforms into martensite.
Although this transformation occurs, the resulting martensite is a body-centered cubic (α) solid solution.
This lattice structure is the same as that of ferrite. Therefore, martensite can still dissolve a large amount of nitrogen.
When a large amount of nitrogen is solidly dissolved in steel, the surface polishing performance is significantly improved.
For this reason, some countries have developed nitrogen-containing plastic mold steel. This type of steel allows the processed mold to achieve an excellent mirror finish.
Obviously, Table 4 in the M303, M333 and M340 should be nitrogen-containing steel.
> Powder metallurgy steel
The steel is formed through powder isostatic pressing followed by high-temperature sintering.
As a result, it contains fewer impurities, has no porosity or segregation, and exhibits isotropic properties.
This steel belongs to the category of ultra-high carbon and alloy martensitic stainless steel.
Its carbon content and the amount of alloying elements are significantly higher than those of ordinary high-carbon martensitic stainless steel.
Because of this composition, the steel possesses very high toughness.
Auxiliary plastic mold steel
Selection of auxiliary plastic mold steel, in addition to the production of a number of less demanding plastic molds, most of which are used for plastic mold accessories.
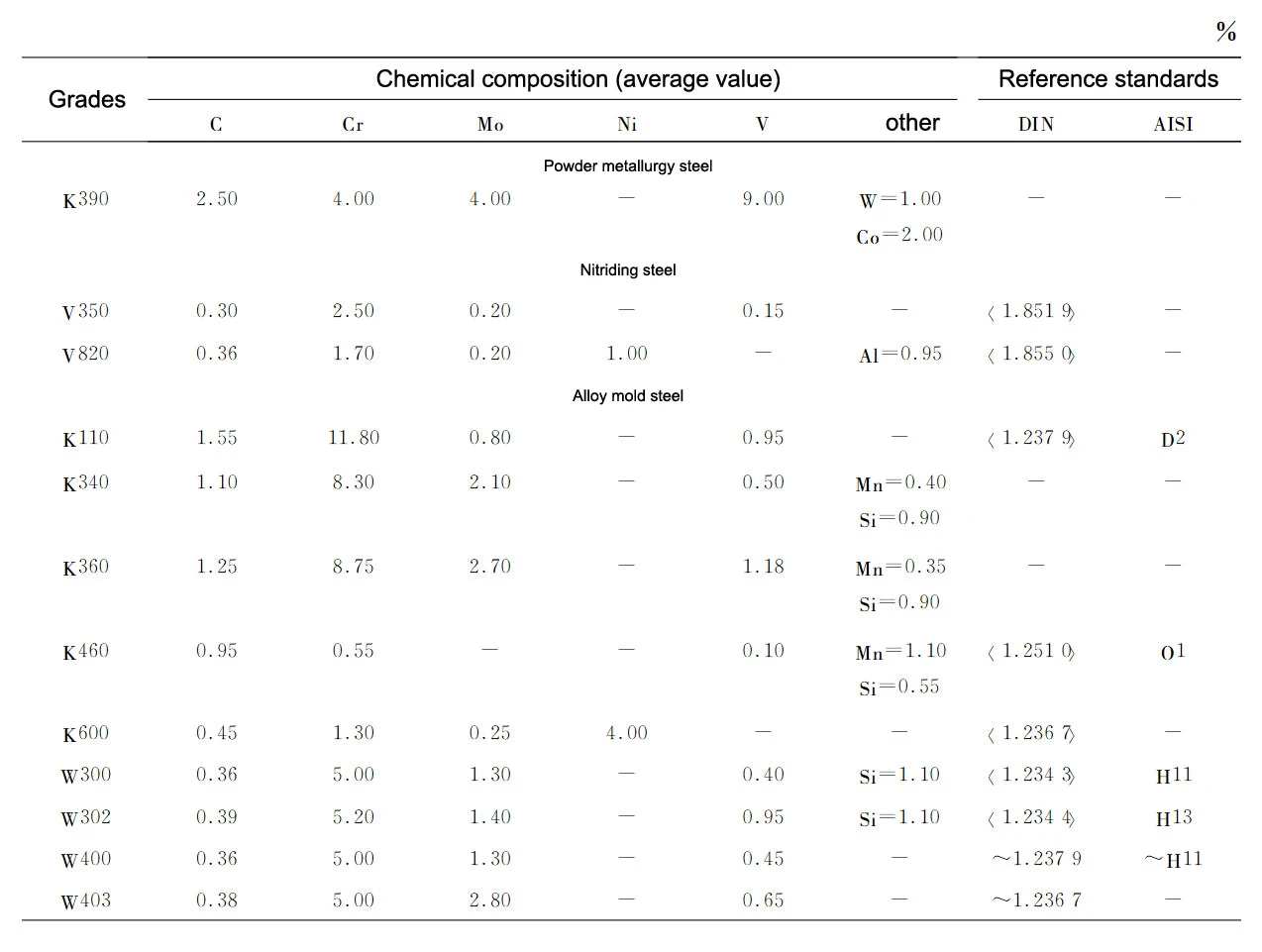
This type of steel can be divided into powder metallurgy steel, nitriding steel and alloy mold steel and other 3 categories, as shown in Table 6.
Plastic mold steel characteristics and uses (see Table 7)
Factors affecting the design of foreign plastic mold steel
Plastic processing temperature
Plastic processing can take place either at room temperature or at high temperatures.
When plastic is processed at room temperature, it tends to cause greater abrasive wear compared to high-temperature processing.
As a result, plastic molds used in such conditions must have high hardness and high strength.
For this reason, steels such as M100 and M130 are designed.
The steel surface carburizing and quenching treatment, the surface hardness of up to 62HRC or so, the heart of the slat martensite so that the steel has high strength.
User’s processing equipment capacity
Mold manufacturers vary in size and capabilities. Many of them only have the ability to perform cold working and lack the facilities for heat treatment.
As a result, they prefer to use molds that can be processed by cold working and then used directly.
Pre-hardened mold steel meets the needs of such users, as it requires no additional heat treatment.
Pre-hardened mold material has reached the hardness of the mold use state, only after cold working directly.
Plastic corrosive
many plastics in the processing will produce sulfide and corrosive gases and other substances, the mold has a strong corrosive, so that the mold life reduced.
Corrosion-resistant plastic mold steel is well equipped with such properties, improve the corrosion resistance of the mold.
Mold processing efficiency
Many mold accessories, such as the mold frame and template, play only an auxiliary role in the complete mold assembly.
Because of this, the performance requirements for these components are not very high. However, they make up a large proportion of the entire mold set.
Because of this, users want to quickly manufacture attachments to improve mold processing efficiency.
The steel with strong chip breaking ability and large feed capacity, i.e., free-cutting steel, can meet such requirements.
Free-cutting steel is by increasing the sulfur content and make steel easy to cut, thus improving the efficiency of steel processing.
High corrosive and abrasive plastics
Many plastics contain both corrosive substances and highly abrasive additives, such as glass fibers.
When general plastic mold steel is used with these materials, it often suffers from severe corrosion and wear.
This leads to a significant reduction in mold life and results in higher processing costs.
To improve the life of the mold, powder metallurgy steel is used, which has high carbon content and a high level of alloying elements.
These properties give the steel very high corrosion resistance and ultra-high abrasion resistance.
By using this steel in the manufacture of plastic molds, the mold life can be extended, and processing costs can be reduced.
Product surface quality requirements
For items like cell phone shells and LCD TV screens, the surface must meet mirror-like quality requirements.
General plastic mold steel, after polishing, often struggles to meet these standards. As a result, a super mirror plastic mold steel is required to achieve the desired finish.
So, add nitrogen in steel to improve the polishing performance of steel, nitrogen-containing steel appeared to solve the problem.
In short, foreign countries fully consider all the factors that affect the design of plastic mold steel.
They take into account the various elements that influence the performance of mold steel during both design and manufacture.
This comprehensive approach helps achieve seamless performance.
Successful mold material supporting model
In addition to the special plastic mold steel, there are auxiliary plastic mold steel available.
Auxiliary materials are not specifically designed for plastic molds, but from other types of steel selected from the most suitable for molds and accessories manufacturing steel.
These materials include powder metallurgy cold work tool steel (e.g. K390), nitrided steel, cold work tool steel (e.g. K110) and hot work die steel (e.g. W302).
Foreign plastic mold auxiliary materials are many types, complete, to achieve a reasonable match of performance, so that the whole set of molds of excellent quality, high life expectancy.
Conclusion
Plastic mold steel types and types, comprehensive performance, to achieve seamless performance distribution, so there is a wide range of options.
It has a successful supporting mode for mold auxiliary materials. The selection of mold auxiliary materials is reasonable, ensuring a good match between the main mold and its auxiliary accessories.
This, in turn, results in a high-quality mold set with a long lifespan.



