Table of Contents
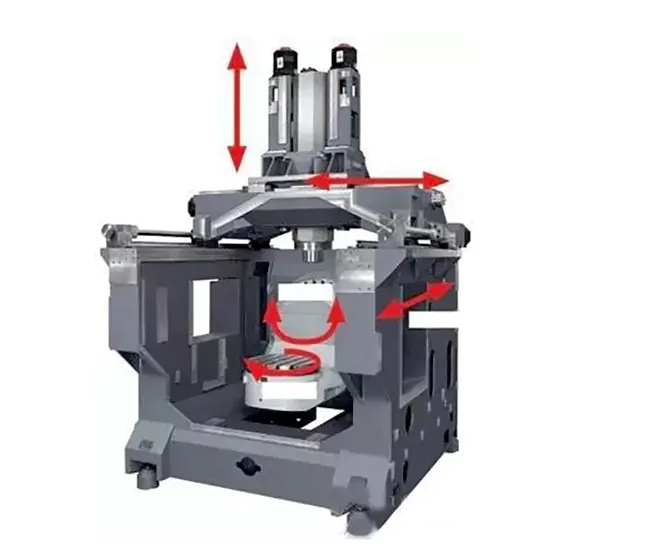
Five-axis machining centers are familiar to industry professionals, featuring five axes of motion: two rotary axes and three linear axes. Based on the positioning of the rotary axes, they are categorized into AC combined rotary axis and BC combined rotary axis. This article focuses on the AC combined rotary axis and its working range.

The working range of the AC rotary axis of the 5-axis machining center
1. A-axis working range: A-axis usually refers to the axis of the five-axis machining center rotating around the X-axis, the working range is +30 degrees to -120 degrees. A-axis rotation allows the machining of beveled surfaces, complex shapes, and parts with special angles.
2. Working range of the C-axis: The C-axis refers to the rotary axis of the 5-axis machining center that rotates around the Z-axis and has a working range of 360 degrees. The C-axis rotation enables 360-degree movement for machining all sides of the workpiece.
The 5-axis machining center can machine all surfaces except mounting surfaces in a single clamping, thanks to the A-axis and C-axis rotation. This setup is particularly suitable for workpieces that require high-precision and high-angle machining.
Advantages of 5-axis machining
1. Complex Surface Machining: Through the 5-axis linkage of A-axis, C-axis, and XYZ linear coordinate axes, the 5-axis machining center can efficiently complete the machining of complex surfaces, including beveled surfaces, beveled holes, and complex three-dimensional shapes. This linkage mechanism makes 5-axis machining an ideal choice for manufacturing complex parts.
2. High accuracy: 5-axis machining centers can avoid angular errors that may occur in traditional 3-axis machining by precisely controlling the rotation angles of the A-axis and C-axis (usually the smallest indexing value is 0.001 degree), ensuring machining accuracy.
3. Reduce the number of workpieces clamping: 5-axis machining centers can complete the machining of multiple surfaces in one clamping process, which greatly reduces the time and error of traditional machining that requires multiple clamping, and improves the machining efficiency.

Structural advantages of AC rotary shaft
AC rotary axes in 5-axis machining centers improve machining accuracy, and efficiency, and reduce costs. The following are the main advantages of the AC rotary axis structure:
1. Simple and rigid structure
AC rotary axis combinations use a simple structure for the A-axis and C-axis, reducing manufacturing costs while enhancing spindle rigidity and support. This rigidity makes the precision during machining more stable and reduces the impact of vibration on machining quality.
2. High machining accuracy
The high-precision design of the AC rotary axis enables the 5-axis machining center to perform precise angular control. The A-axis and C-axis typically have a minimum indexing value of 0.001 degrees, allowing precise control of machining angles. This makes the AC rotary axis ideal for complex shapes, inclined surfaces, and holes, avoiding precision loss from frequent clamping in traditional three-axis machining.
3. Improved tooling efficiency
The AC rotary axis’s rotation angle and flexibility allow the tool to contact the workpiece from multiple angles, reducing local wear, improving tool surface usage, and extending tool life, which lowers replacement frequency and cost.
4. Saving machining time
The AC rotary axis combination enables machining multiple surfaces in a single clamping by rotating the workpiece on the A and C axes, reducing clamping time and cycle times.
5. Machining complex workpieces
The AC rotary axis enables 5-axis machining to work in multiple directions simultaneously, ideal for complex parts like curved shapes, angled holes, and intricate geometries. It offers greater flexibility than traditional 3-axis machining, supporting a wider variety of workpiece shapes.
6. Reduced tool interference
The rotation of the A-axis and C-axis allows the tool to reach the optimal position, avoiding interference issues in conventional 3-axis machining. This AC rotary axis ensures tool movement at multiple angles, preventing tool-workpiece interference and improving machining stability and safety.
7. Machining fine details and high-quality surfaces
The AC rotary axis enables cutting at multiple angles, ensuring more uniform tool contact, reducing surface roughness and tool marks, and improving surface finish, which is crucial for high-quality parts like molds and precision components.
8. Improved machining stability
The AC rotary axis offers better rigidity and fewer mechanical errors, ensuring stability during high-speed cutting, crucial for high-precision operations like aerospace and automotive components.
9. Reduced mechanical wear
The AC rotary axis design prevents excessive wear from uneven cutting, distributing forces more evenly and extending equipment and tool life.
10. Adaptable to a wide range of machining needs
AC rotary axes offer flexibility and precision for machining complex shapes and materials, including aluminum, titanium alloys, stainless steel, and other hard materials.
Disadvantages and Limitations of AC Combination Rotary Axis
1. Limited table load capacity
The AC Combination Rotary Axis table cannot be too large and has a low load capacity. When the A-axis reaches 90 degrees or more, the loading moment can be very large, potentially causing table deformation or an inability to support heavy workpieces.
2. Load Moment Problem
When the A-axis rotates to larger angles (e.g., 90 degrees or more), the resulting gravity-induced load can affect the stability and accuracy of machining, potentially damaging the table and equipment. Special attention is needed in 5-axis machining to avoid excessive load.
3. Limited working range
The AC combined rotary axis has a smaller working range than the BC axis, which may limit certain processes requiring larger angles or more rotation freedom.
4. Structural complexity and maintenance
The AC Combined Rotary Axis is simple, but the overall complexity of a 5-axis machining center is high. Its multi-axis system requires precise control and coordination, making repairs and adjustments difficult. The high precision of the rotary axes also increases maintenance and repair costs.
5. Accuracy and stability challenges
External factors like temperature changes, mechanical wear, and cutting force variations can affect the AC rotary axis rotation during machining g. The accuracy and stability of the rotary axis may be affected especially during long time and high load machining. This may cause fluctuations in machining accuracy for workpieces with high requirements for precision machining and high-quality surface treatment.
6. High demands on the CNC system
AC combined rotary axes require a high-precision CNC system to coordinate the A-axis, C-axis, and XYZ-axis linkage control. This requires a high response speed of the CNC system and the accuracy of the algorithms. Poor performance of the CNC system may result in unstable machining or failure to achieve the desired accuracy. The high requirements for the CNC and servo motor systems raise equipment costs and usage thresholds.

Conclusion
The five-axis machining center’s AC rotary axis combination offers a simple structure, good rigidity, and low cost. It is especially suitable for the machining of complex curved surfaces, slanted surfaces, and three-dimensional shapes. The table load capacity and load torque may limit machining capability, so these factors should be considered in design and use. With precise CNC control and servo motors, the AC Combined Rotary Axis enables efficient, accurate 5-axis machining, ensuring high-precision part manufacturing.